Introduction to Hybrid Caching in ASP.NET Core
Caching is a technique used to store frequently accessed data in temporary locations so it can be accessed faster. Caching can significantly improve the performance and scalability of an application by reducing the time it takes to generate content. In this article, we will explore hybrid caching, a new feature introduced in ASP.NET Core 9.
Caching in ASP.NET Core
ASP.NET Core traditionally supports two types of caching: in-memory caching and distributed caching.
In-Memory Caching
In-memory caching, also referred to as L1 caching uses the application server’s memory to store the data. This type of caching is suitable for single-server applications, or multiple-server applications that use session affinity (aka. sticky sessions - these guarantee that requests from the same client are always routed to and processed by the same server) . In-memory caching is fast and efficient but has limitations when it comes to scalability and reliability.
Distributed Caching
A distributed cache, also known as an L2 cache, is a cache shared across multiple servers. It is used to store data that is accessed frequently and needs to be shared across multiple instances of an application. A distributed cache is typically maintained as an external service to the application servers that access it. Examples of distributed caching services include Redis, NCache, and SQL Server.
Distributed caching is more scalable and reliable than in-memory caching but can be slower due to network latency.
Hybrid Caching
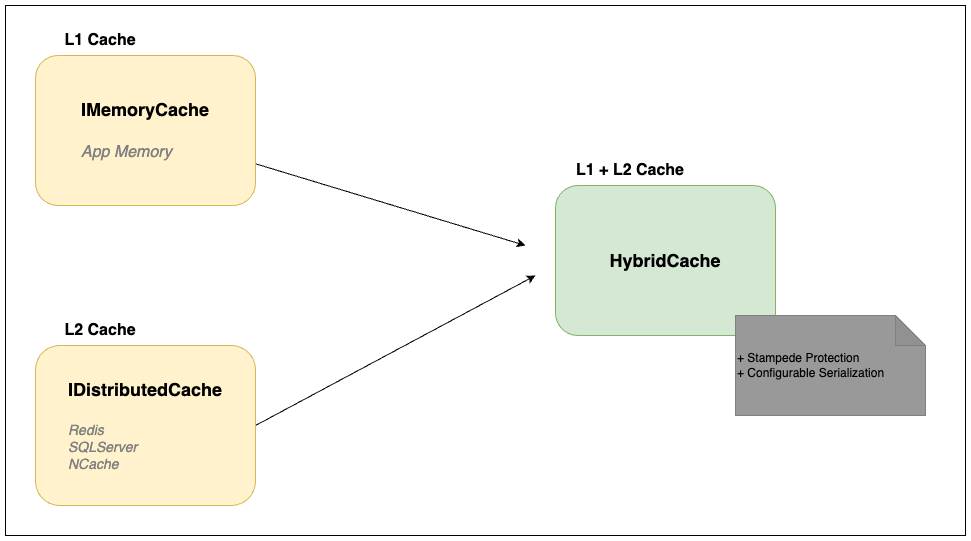
The HybridCache API is designed to bridge the gaps of the IDistributedCache and the IMemoryCache APIs. It is designed to have the speed of the in-memory cache and the durability of the distributed cache. HybridCache combines both the in-memory and distributed caching strategies and adds more advanced features, including:
- Two-level caching strategy: Use in-memory cache as the primary cache storage and distributed cache as the secondary storage.
- Stampede Protection: A cache stampede occurs when frequently accessed data expires and multiple requests attempt to repopulate the cache with the same entry at the same time.
HybridCachecombines concurrent operations to prevent cache stampedes. Requests that attempt to repopulate the cache with the same entry will be blocked until the first request is completed and will wait for the result of that request. - Configurable Serialization:
HybridCacheallows you to configure the serialization format used to store data. By default, the service handlesstringandbyte[]and usesSystem.Text.Jsonfor serialization and deserialization.HybridCachecan be configured to use other types of serializers, such asprotobuforXML
Finally, HybridCache provides an intuitive and easy-to-use GetOrCreateAsync method that allows you to retrieve data from the cache or generate it if it does not exist.
When using the IDistributedCache, the typical workflow is as follows:
- attempt to read data from the cache (as
byte[]) - check if the read data is
null- if the data is
null,- generate the data
- store it in the cache
- return the data
- if the data is
You can have code that looks like this:
app.MapGet("/data", async (IDistributedCache distributedCache) =>
{
string? data = null;
var dataBytesArray = await distributedCache.GetAsync("data-key");
if ((dataBytesArray?.Length ?? 0 ) > 0)
{
data = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(dataBytesArray);
var deserializedData = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<string>(data);
return deserializedData;
}
var dataFromSource = await GenerateDataAsync();
data = JsonSerializer.Serialize(dataFromSource);
dataBytesArray = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(data);
await distributedCache.SetAsync("data-key", dataBytesArray);
return dataFromSource;
});
private async Task<string> GenerateDataAsync()
{
// Generate data
return Task.FromResult("Hello, World!");
}
The GetOrCreateAsync method simplifies this workflow by combining the read, check, and write operations into a single method call.
Install the Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Hybrid package to use the HybridCache.
$> dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Hybrid --prerelease
app.MapGet("/data", async (HybridCache hybridCache) =>
{
return await hybridCache.GetOrCreateAsync("data-key",
factory: async cancel => await GenerateData());
});
The GetOrCreateAsync method will use the key to attempt and retrieve the data from the primary cache (memory cache). If the item is not found in the primary cache (we have a cache miss), it then checks the secondary cache if one is configured. If the data is not found there as well, the factory method is called to get the data from the original data source. The data is then stored in both the primary and secondary caches. The data factory is never called again if the data is found in the primary or secondary caches.
If concurrent calls are made to the GetOrCreateAsync method with the same key and the data is not found in the cache, only the first call will make a call to the factory method. The other calls will wait for the first call to complete and return the data from the cache. The key used must be unique to identify the data retrieved from the data source, and also unique compared to the other data stored in the cache.
HybridCache also provides a SetAsync method that allows us to store data in the cache without trying to retrieve it first.
app.MapGet("/data", async (HybridCache hybridCache) =>
{
var data = await GenerateDataAsync();
await hybridCache.SetAsync("data-key", data);
return Results.Ok(data);
});
We can use the RemoveAsync method to remove data from the cache. Data is removed from both the primary and secondary caches.
app.MapDelete("/data/{id}", async (int id, HybridCache hybridCache) =>
{
await DeleteDataAsync(id);
await hybridCache.RemoveAsync($"data-key-{id}");
return Results.NoContent();
});
To add a distributed cache to use as a secondary cache, we can add it how we normally add a distributed cache. HybridCache will detect the presence of the distributed cache and use it as the secondary cache. To add Redis as a distributed cache, we can add the following code to the Startup class.
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.StackExchangeRedis
builder.Services.AddStackExchangeRedisCache(options =>
{
options.Configuration = "<redis-connection-string>";
});
builder.Services.AddHybridCache();
Conclusion
HybridCache offers a robust caching solution that combines the speed of in-memory caching and the durability of distributed caching. It simplifies the caching process by providing an easy-to-use API that handles cache misses, cache stampedes, and serialization. By using HybridCache, you can improve the performance and scalability of your ASP.NET Core applications.
HybridCache is still in preview and is expected to be released after .NET 9.0. I also came across FusionCache, an open-source library that provides a similar caching solution. FusionCache is production-ready and can be used in your applications today.